Umesh Kumar Pandey & Dr. Vivek Kr Singh, 17 May 2024
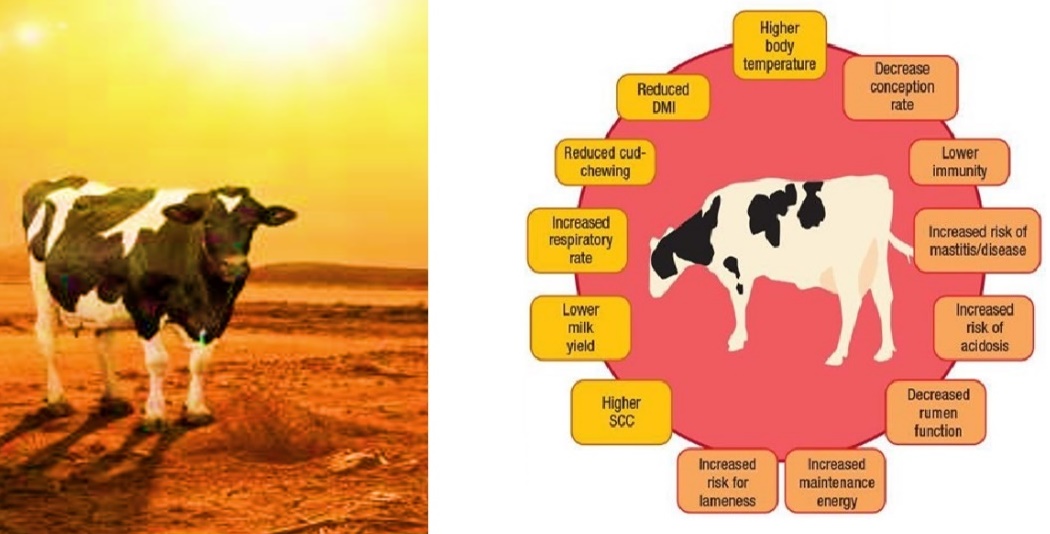
Summer poses unique challenges for dairy farmers, impacting the milk production of their animals due to various factors. One of the primary hurdles faced during this season is the scarcity of green fodder. As the temperatures rise and crops are harvested, the availability of lush grazing material dwindles. This shortage directly affects the nutritional intake of dairy animals, leading to insufficient nourishment and consequently, a decline in milk production.
In addition to the scarcity of green fodder, dairy animals experience significant physiological changes during the summer months. Hormonal fluctuations and variations in pH levels within their bodies can trigger stress responses. This stress often manifests through increased saliva production and the expulsion of alkaline substances, disrupting the animals' digestive processes and diminishing their appetite. Consequently, these physiological disruptions contribute to reduced milk output.
To address these challenges, veterinary experts emphasize the importance of implementing comprehensive care strategies for dairy animals during the summer. Providing shaded areas where animals can seek refuge from the scorching heat is essential to prevent heat stress. Regularly bathing the animals with cool water before sunrise and after sunset aids in temperature regulation and alleviates heat-induced discomfort. To help prevent heat stroke, it's important to drink plenty of water mixed with jaggery, a rich source of glucose. Ensure the water is clean, fresh, and changed daily to prevent bacterial growth. With the new crop harvested this season, the chaff is highly enriched with phosphorus but has low protein content, which can lead to indigestion. Therefore, it's recommended to administer antidiarrheal drugs and digestive tonics.
Furthermore, supplementing the animals' diets with specialized nutritional products designed for dairy animals, such as MINROL 21 and PV-MIL-21, can help maintain their health and support consistent milk production during the summer months. These supplements are formulated to provide essential nutrients that may be lacking in the animals' diet due to the scarcity of green fodder.
Farmers are also encouraged to cultivate diverse types of green fodder in their fields to ensure a continuous and quality food supply for their animals. Growing a variety of forage plants can help mitigate the impact of seasonal fluctuations and provide a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients. This proactive approach not only supports the health and well-being of dairy animals but also contributes to sustaining milk production levels despite the challenges posed by summer.
In conclusion, understanding the specific challenges that dairy animals face during the summer is crucial for devising effective solutions to optimize milk production and ensure animal welfare. By addressing issues such as the scarcity of green fodder, hormonal fluctuations, and heat stress through strategic care practices and nutritional interventions, farmers can mitigate the negative impact of summer on milk production and maintain the overall health and productivity of their dairy herds. This holistic approach underscores the importance of proactive management and informed decision-making in the dairy farming industry, especially during challenging seasonal conditions.